Deploying EasyNav on a Real iCreate3 Robot
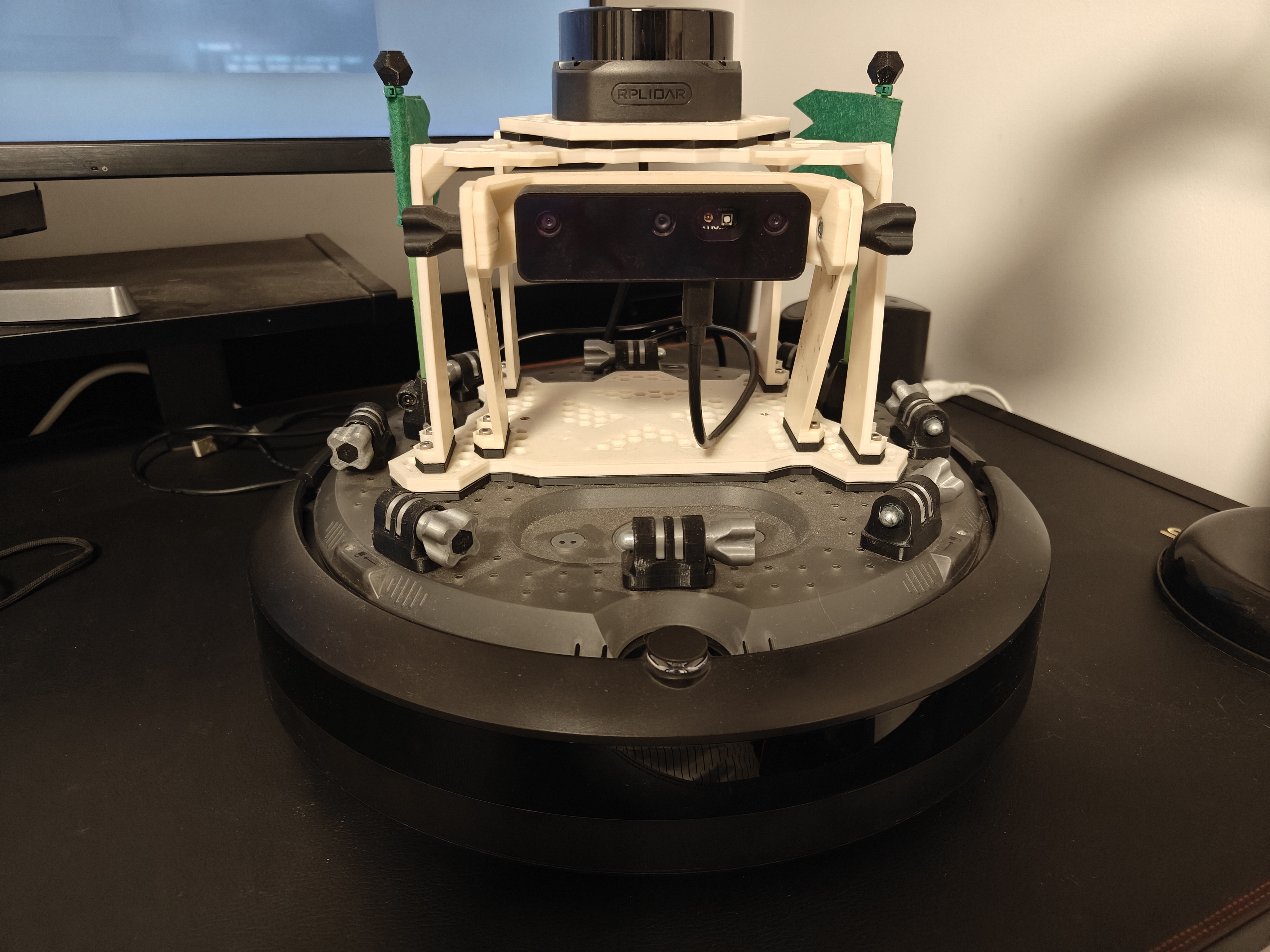
Hardware Setup
Note
The overall workflow mirrors the one in the Simple Stack tutorials, but here you will run on real hardware. The representation used by the navigation stack is a graded Costmap2D.
Base: iRobot iCreate3. Use the vendor instructions to connect to Wi‑Fi and update firmware. We used the latest firmware for ROS 2 Iron with FastDDS: https://edu.irobot.com/create3-latest-fw
Laser: RPLidar S2 mounted on top of the base.
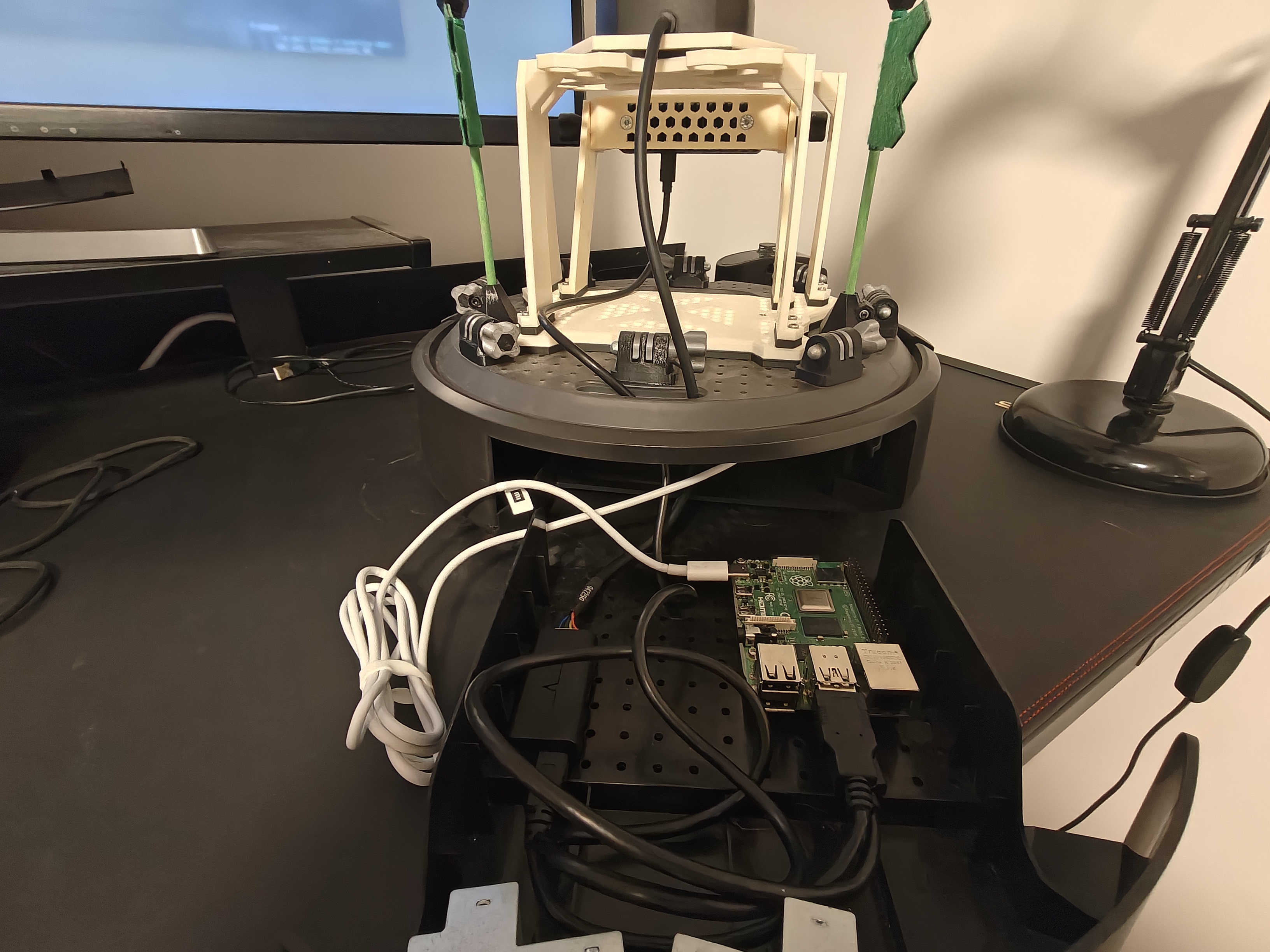

On‑board computer: Raspberry Pi 4 Model B powered from the base over USB‑C. Ethernet‑over‑USB‑C was not available in our setup, so the Raspberry communicates with the base over Wi‑Fi. The LIDAR is connected directly to the Raspberry Pi via USB. The Raspberry Pi is flashed with Ubuntu 24.04 Desktop following https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi and uses the Kilted ROS 2 distribution.
Operator laptop: runs
rviz2and is used to SSH into the Raspberry Pi to launch processes.
ROS 2 Setup on the Raspberry Pi
Follow the official steps at https://docs.ros.org/en/kilted/Installation/Ubuntu-Install-Debs.html. In short:
Enable the Ubuntu universe repository
ir@raspberrypi:~$ sudo apt install -y software-properties-common
ir@raspberrypi:~$ sudo add-apt-repository -y universe
Configure ROS 2 repositories
ir@raspberrypi:~$ sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y curl
ir@raspberrypi:~$ export ROS_APT_SOURCE_VERSION=$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/ros-infrastructure/ros-apt-source/releases/latest | grep -F "tag_name" | awk -F\" '{print $4}')
ir@raspberrypi:~$ curl -L -o /tmp/ros2-apt-source.deb "https://github.com/ros-infrastructure/ros-apt-source/releases/download/${ROS_APT_SOURCE_VERSION}/ros2-apt-source_${ROS_APT_SOURCE_VERSION}.$(. /etc/os-release && echo $VERSION_CODENAME)_all.deb"
ir@raspberrypi:~$ sudo dpkg -i /tmp/ros2-apt-source.deb
Install development tools and ROS 2
ir@raspberrypi:~$ sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y ros-dev-tools
ir@raspberrypi:~$ sudo apt update && sudo apt -y upgrade
ir@raspberrypi:~$ sudo apt install -y ros-kilted-desktop
Install additional packages
ir@raspberrypi:~$ sudo apt install -y openssh-server \
ros-kilted-rplidar-ros \
ros-kilted-depthai ros-kilted-depthai-ros ros-kilted-depthai-ros-driver ros-kilted-depthai-bridge \
ros-kilted-slam-toolbox \
ros-kilted-rmw-zenoh-cpp ros-kilted-zenoh-cpp-vendor \
ros-kilted-tf2-ros ros-kilted-tf2-py ros-kilted-tf2-tools \
ros-kilted-irobot-create-msgs
EasyNav Setup on the Raspberry Pi
Create the workspace
ir@raspberrypi:~$ mkdir -p ~/easynav_ws/src
ir@raspberrypi:~$ cd ~/easynav_ws/src
Clone the required repositories
ir@raspberrypi:~/easynav_ws/src$ git clone https://github.com/EasyNavigation/easynav_plugins.git
ir@raspberrypi:~/easynav_ws/src$ git clone https://github.com/EasyNavigation/easynav_costmap_stack.git
ir@raspberrypi:~/easynav_ws/src$ git clone https://github.com/EasyNavigation/easynav_indoor_testcase.git
ir@raspberrypi:~/easynav_ws/src$ git clone --recursive https://github.com/EasyNavigation/EasyNavigation.git
ir@raspberrypi:~/easynav_ws/src$ git clone https://github.com/Slamtec/sllidar_ros2.git
Install dependencies
ir@raspberrypi:~/easynav_ws/src$ cd ..
ir@raspberrypi:~/easynav_ws$ rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the workspace
ir@raspberrypi:~/easynav_ws$ colcon build --symlink-install
Source in
~/.bashrc
ir@raspberrypi:~$ echo 'source /opt/ros/kilted/setup.bash' >> ~/.bashrc
ir@raspberrypi:~$ echo 'source ~/easynav_ws/install/setup.bash' >> ~/.bashrc
ir@raspberrypi:~$ source ~/.bashrc
Mapping
Verify that both the laptop (argo) and the Raspberry Pi can see the base topics
fmrico@argo:~$ ros2 topic list
ir@raspberrypi:~$ ros2 topic list
You should see topics such as /odom, /tf, /tf_static, /battery_state, and others exposed by the iCreate3.
Publish the static transform from the base to the laser
ir@raspberrypi:~$ ros2 run tf2_ros static_transform_publisher \
--x 0.02 --z 0.22 --yaw 3.14 \
--frame-id base_link --child-frame-id laser
Keep this process running during mapping and navigation.
Start the laser driver
ir@raspberrypi:~$ ros2 launch sllidar_ros2 sllidar_s2_launch.py
Keep this process running during mapping and navigation.
Place the robot at the position that you want to be
(0, 0)in the map (remember it), and start SLAM Toolbox on the Raspberry Pi
ir@raspberrypi:~$ ros2 launch slam_toolbox online_async_launch.py
On the laptop, open RViz2
fmrico@argo:~$ rviz2
Open a teleop to move the robot while mapping
fmrico@argo:~$ ros2 run teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard
Drive the robot until the map is complete, then save the map
ir@raspberrypi:~/easynav_ws$ ros2 service call /slam_toolbox/save_map slam_toolbox/srv/SaveMap
Store the generated
.yamland image file (.pgm/.png) under/home/ir/easynav_ws/src/easynav_indoor_testcase/maps. You may rename the map file, but ensure the image filename inside the YAML is updated accordingly.
Tip
If you need to reset the odom → base_footprint transform on iCreate3, call:
ir@raspberrypi:~$ ros2 service call /reset_pose irobot_create_msgs/srv/ResetPose
Navigation
Repeat steps (2) and (3) from Mapping if you closed the static transform publisher or the laser driver.
Verify the parameter file at
/home/ir/easynav_ws/src/easynav_indoor_testcase/robots_params/costmap.serest.params.yaml.
Ensure the map path points to your saved map (for example, maps/casa.yaml) and that filter plugin names are correct
(see notes below).
controller_node:
ros__parameters:
use_sim_time: false
controller_types: [serest]
serest:
rt_freq: 30.0
plugin: easynav_serest_controller/SerestController
allow_reverse: true
max_linear_speed: 0.8
max_angular_speed: 1.2
d0_margin: 0.2
d_hard: 0.15
v_progress_min: 0.08
k_s_share_max: 0.5
k_theta: 2.5
k_y: 1.5
goal_pos_tol: 0.1
goal_yaw_tol_deg: 6.0
slow_radius: 0.60
slow_min_speed: 0.03
final_align_k: 2.0
final_align_wmax: 0.6
corner_guard_enable: true
corner_gain_ey: 1.8
corner_gain_eth: 0.7
corner_gain_kappa: 0.4
corner_min_alpha: 0.35
corner_boost_omega: 1.0
a_lat_soft: 0.9
apex_ey_des: 0.05
localizer_node:
ros__parameters:
use_sim_time: false
localizer_types: [costmap]
costmap:
rt_freq: 50.0
freq: 5.0
reseed_freq: 1.0
plugin: easynav_costmap_localizer/AMCLLocalizer
num_particles: 100
compute_odom_from_tf: true
noise_translation: 0.01
noise_rotation: 0.01
noise_translation_to_rotation: 0.01
min_noise_xy: 0.02
min_noise_yaw: 0.02
initial_pose:
x: 0.0
y: 0.1
yaw: 0.0
std_dev_xy: 0.02
std_dev_yaw: 0.02
maps_manager_node:
ros__parameters:
use_sim_time: false
map_types: [costmap]
costmap:
freq: 10.0
plugin: easynav_costmap_maps_manager/CostmapMapsManager
package: easynav_indoor_testcase
map_path_file: maps/casa.yaml
filters: [obstacles, inflation]
obstacles:
plugin: easynav_costmap_maps_manager/ObstacleFilter
inflation:
plugin: easynav_costmap_maps_manager/InflationFilter
inflation_radius: 0.4
cost_scaling_factor: 2.0
planner_node:
ros__parameters:
use_sim_time: false
planner_types: [simple]
simple:
freq: 2.0
plugin: easynav_costmap_planner/CostmapPlanner
cost_factor: 10.0
# continuous_replan: false
sensors_node:
ros__parameters:
use_sim_time: false
forget_time: 0.5
sensors: [laser1]
perception_default_frame: odom
laser1:
topic: scan
type: sensor_msgs/msg/LaserScan
group: points
camera1:
topic: rgbd_camera/points
type: sensor_msgs/msg/PointCloud2
group: points
system_node:
ros__parameters:
use_sim_time: false
use_real_time: true
position_tolerance: 0.1
angle_tolerance: 0.05
Start EasyNav (on the Raspberry Pi):
ir@raspberrypi:~$ ros2 run easynav_system system_main \
--ros-args --params-file /home/ir/easynav_ws/src/easynav_indoor_testcase/robots_params/costmap.serest.params.yaml
Notes
Filter plugin names in the maps manager must match the class types: use
easynav_costmap_maps_manager/ObstacleFilterandeasynav_costmap_maps_manager/InflationFilter.The Costmap Planner parameters include
cost_factor(and others such ascost_axial,cost_diagonal,inflation_penalty, andcontinuous_replan). Adjust them to your environment if necessary.