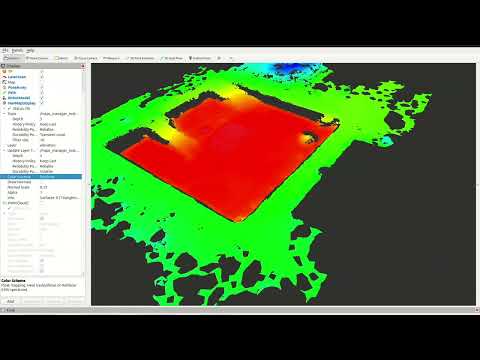
NavMap is an open-source C++ and ROS 2 library for representing navigable surfaces for mobile robot navigation and localization. Unlike classic grid-based maps, NavMap stores the environment as triangular meshes (NavCels), enabling efficient queries and multi-surface environments (e.g., multi-floor buildings).
✨ Features
- Triangular cell mesh representation with adjacency relations.
- Dynamic runtime layers: per-cell or per-vertex attributes (occupancy, elevation, cost, traversability, etc.).
- Locate API: find the NavCel under/around a 3D position using BVH acceleration and raycasting.
- Raytracing: Möller–Trumbore intersection with a simple BVH for efficiency.
- Multi-surface support: naturally supports multiple disconnected surfaces (e.g., separate floors).
📂 Repository structure
This repository is organized into several ROS 2 packages:
navmap_core/
Core C++ library implementing NavMap. Minimal dependencies (Eigen3).navmap_ros/
ROS 2 conversions and message definitions:
navmap::NavMap↔navmap_ros_interfaces::msg::NavMap
nav_msgs::msg::OccupancyGrid↔navmap::NavMap
navmap_rviz_plugin/
RViz2 plugin for visualization of NavMap messages:
- Displays surfaces and layers.
- Optional per-cell normal rendering.
- Layer-based coloring.
- Displays surfaces and layers.
navmap_tools/
Tools and utilities for building and testing NavMaps (mesh import/export, conversions, etc.)navmap_examples/
Practical examples demonstrating the usage of NavMap, both core C++ API and ROS 2 integrations.
⚙️ Build instructions
NavMap can be built as a standalone C++ library or within a ROS 2 workspace.
ROS 2 colcon build
Dependencies
- C++23 compiler
- Eigen3
- ROS 2 (tested with Humble, Iron, Jazzy)
- RViz2 (for the visualization plugin)
- PCL (for mesh construction utilities)
🚀 Usage (C++ API)
This section shows small, self-contained snippets that demonstrate how to create a NavMap, add geometry, attach layers, query values, and locate the triangle (NavCel) corresponding to a 3D position.
Note: After modifying geometry (vertices, triangles, or surfaces), always call
rebuild_geometry_accels()before performing queries such aslocate_navcel()orraycast().
1. Create a minimal NavMap (single square floor with two triangles)
2. Add a per-NavCel layer (cost or occupancy)
3. Read a layer value for a given NavCel
4. Locate the NavCel corresponding to a 3D position
5. Sample a layer at a world position
If the layer does not exist or the position cannot be located, the fallback value (-1.0 here) is returned.
6. Raycasting
7. Marking areas (set_area)
You can set values over regions of the map using shapes such as circular or rectangular areas:
8. Serialize to / from ROS messages
Conversion functions are provided in navmap_ros:
9. Save and load from disk
NavMap supports saving and loading using YAML + mesh files:
10. Classic low-level API
For advanced control you can still access internal data directly:
📦 Usage (Examples package)
In addition to the snippets above, the repository provides the package navmap_examples with ready-to-run executables.
Build
If your navmap_core / navmap_ros do not yet export CMake targets, you can provide include paths:
Disable ROS 2 examples:
Run core examples
Each demonstrates a different feature: geometry creation, multi-surface, U8/F32 layers, centroids and neighbors, area marking, raycasting, and copy/assign semantics.
Run ROS 2 examples
If BUILD_ROS_EXAMPLES=ON:
Or via launch:
🧪 Testing
NavMap provides unit tests with GTest. To run them:
🤝 Contributing
Contributions are welcome! Please open issues and pull requests on GitHub.
Before submitting code, run the linters and tests:
📜 License
This project is licensed under the Apache 2 License.
See the [LICENSE](LICENSE) file for details.
🙏 Acknowledgements
Developed at the Intelligent Robotics Lab (Universidad Rey Juan Carlos).
Part of the Easy Navigation (EasyNav) project.
Generated by